Different Types of Brick for Construction
Bricks stand as one of the most ancient and adaptable building materials employed in construction endeavors. Widely utilized for erecting walls, pavements, and various structures, bricks come in diverse types, each tailored to specific engineering and architectural requirements.
Different Types of Bricks
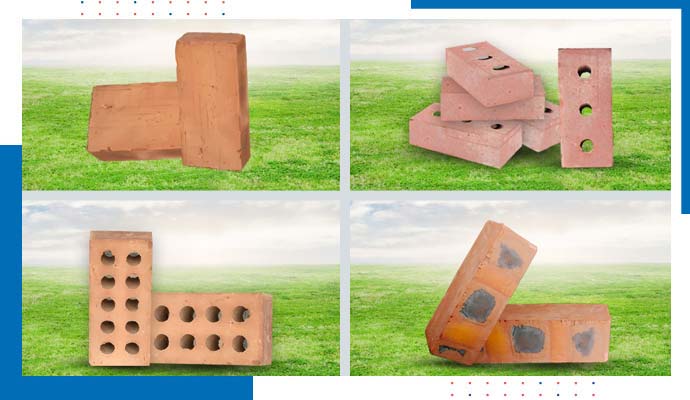

We can break down the list of the different types of bricks into 5 different classes. Bricks come in various sizes, colors, and types, each with specific properties suited for different applications. We will discuss the types of bricks for engineering purposes, processing methods, class, materials, and Weather-resistance level.
Engineering Purposes
Solid Bricks: Solid Bricks are the most basic bricks, typically made from clay and sand. They are used for general construction purposes and are usually red or brown.
Hollow Bricks: Hollow bricks are lightweight and have holes inside them, which reduce their weight and improve their insulation properties. They are commonly used in load-bearing walls. Hollow bricks are mainly three types-
Engineering Bricks: Engineering bricks are known for their high strength and low water absorption properties. They are often used in applications where durability and load-bearing capacity are essential, such as retaining walls and foundations.
Beautification Bricks: These bricks add charm to a place. For instance, sidewalks, parks, and delightful architectural buildings use them. Clay, ceramic, calcium silicate, and concrete bricks fall into this category.
Processing Methods
Sun-Burnt Bricks: Sun-burnt brick, also known as sun-dried brick or adobe, is a building material made from natural clay or earth that is shaped into bricks and dried in the sun. These bricks are left under the sun after molding. This method is very popular in Bangladesh.
Burnt Bricks: They are burnt in kilns and have four grades. This process results in a durable and sturdy material that is commonly used in construction for walls, pavements, and other structural elements.
Automated Machine Bricks: Automated machine bricks are manufactured using automated machinery in controlled industrial settings. This modern brick production method contrasts with traditional brick-making techniques that rely on manual labor and sun-drying processes.
Extruded Bricks: They have standard shapes and sizes. Clay and water go into a steel die to make them. These are the best solutions for limited-budget constructions.
Molded Bricks: Molded bricks, also known as pressed bricks, are a type of brick that is formed by pressing clay or other raw materials into molds under high pressure. This manufacturing process results in bricks with consistent dimensions and smooth surfaces, making them ideal for construction projects.
Dry-pressed Bricks: These are also known as simply pressed bricks. This method results in bricks with precise dimensions, sharp edges, and a smooth surface finish, making them suitable for various construction applications.

Brick Class
First-class Bricks: High strength and long-lasting are the two foremost features. Table molding gives them quality.
Second-class Bricks: Although they possess irregular shapes and textures due to ground molding, exhibit commendable durability and reliability in performance.
Third-class Bricks: Akin to unburnt bricks in strength, are primarily employed in temporary constructions due to their transient nature.
Fourth-class Bricks: Characterized by their inferior quality, are deemed unfit for significant engineering projects. Instead, they are crushed into pieces and incorporated into concrete mixtures as filler material.
Raw Materials
Fly Ash Bricks: These bricks are made from fly ash, a byproduct of coal combustion, mixed with cement and water. They are known for their strength, durability, and eco-friendliness, making them a popular choice in sustainable construction projects.
Sand Lime Bricks: Also known as calcium silicate bricks, sand lime bricks are made from sand, lime, and water. They are highly durable and moisture resistant and often used in coastal areas or where high humidity levels are present.
Concrete Bricks: Concrete bricks are made from a mixture of cement, sand, and aggregate, which is moulded into shape and then cured under controlled conditions. They are widely used in both residential and commercial construction due to their strength, versatility, and affordability.
Ceramic Bricks: Ceramic bricks are a type of brick made from ceramic materials, typically clay, which are fired at high temperatures to produce a durable and versatile building material.

Weather Resistance level
Severe Weather Grade: Countries with harsh climates need them to dodge the effects of snow, blizzards, and rain. They avert freeze and thaw impacts.
Moderate Weather Grade: Tropical countries benefit from them. They can handle high temperatures.
Weather Neutral Grade: These bricks are devoid of weather-resistance features. They go into the interiors.

Some Key Features of Bricks
Bricks, as a building material, possess several distinctive features that make them a preferred choice in construction. Here are some key features of bricks:
Durability: Bricks are renowned for their durability. When properly manufactured and laid, they can withstand various weather conditions, including extreme heat, cold, rain, and wind.
Strength: Bricks have excellent compressive strength, which makes them capable of bearing heavy loads. This strength is crucial for structural stability in buildings, walls, and other construction elements. A standard-size brick can withstand approximately 400,000 lbs.
Fire Resistance: Many types of bricks, such as fire bricks and engineering bricks, exhibit high resistance to fire. This property makes them ideal for use in fireplaces, chimneys, and other applications where exposure to high temperatures is expected.
Cost Effectiveness: Despite initial costs, brick's durability, longevity, and low maintenance requirements often result in long-term cost savings for property owners.
Last Words
Various categories of bricks exist based on their structural components, each offering distinct properties, uses, and suitability across construction projects. This classification aids in selecting the appropriate brick for residential homes or futuristic commercial structures.